Ball a of Mass 5.0 Kilograms Moving at 20
After the collision ball A moves at 10. Ball A has mass 50 kg and is moving at -32 ms when it strikes stationary ball B which has mass 39 kg in a head-on collision.

A Ball Of 0 20kg Hits A Wall At An Angle Of 45 With A Velocity Of 25 Ms 1 If The Rebounds At 90 To The Direction Of Incidence Calculate The Change In
Meters per second and ball B at 15 meters per second both still in the same direction.

. What is the mass of ball B. After the collision ball A moves at 10. While driving down a road in your car that has a mass of 1300 kg you.
A ball of mass 0. Meters per second in the same direction. Meters per second and ball B at 15 meters per second both still in the same direction.
Meters per second collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10. Would doubling the mass or doubling the speed have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of the ball. A 40-kilogram mass is moving across a horizontal surface at 50 meters per second.
An 50-kg ice skater moving at 10 ms east hits a 25-kg ice skater at rest. A ball with a mass of 50 g is moving at a speed of 20 ms. Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20.
Explane in which case Fahas a maximum Value minimum Value in Pulling the car shown in Fig 20. Kg with ball B of unknown mass movingat 10. One ball of mass m_15 kg moving at u_12 ms hits another ball of mass m_23 kg at rest u_20.
Meters per second collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10. After the collision ball A moves at 10. What is the mass of ball B.
Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20 meters per second collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10 meters per second in the same direction. A ball with a mass of 50 g is moving at a speed of 20 ms. 12 Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20.
Meters per second in the same direction. Force on a 30-kilogram roller-skater for 020 second. C If the collision is completely inelastic.
Meters per second in the same direction. A 025 s B 10 s o sos D 20 s 60. Answer choices 60 kg 20 kg 10 kg 12 kg.
If F is opposed to u A 180 cosA -1 so. Meters per second collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10. Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20 ms collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10 ms in the same direction.
And initial velocity u 20 ms. A After the collision ball A moves at 10 ms and ball B at 15 ms both still in the same direction. V 195 ms.
What is the velocity of the ball of mass 50 kg after the collision. Class 11 Physics Laws of Motion Newtons Second Law of Motion. A 20-kg ball moving at 10 ms makes an off-center collision with a 30-kg ball that is initially at rest.
If force F is parallel to u A 0 cosA 1 so. CLASSES AND TRENDING CHAPTER class 5. After collision the first ball stops ie.
By the conservation of momentum in moving direction of first ball. 5 s calculate the. 6 An object of mass 14 kg is moving at a velocity of 50 ms and hits head-on and elastically a stationary ball with a mass of 50 kg.
V 205 ms. After the collision ball A moves at 10 meters per second and ball B at 15 meters per second both still in the same direction. If the collision is perfectly elastic what will be the speed and direction of each ball after the.
If the ball has remained in contact with the wall for 0. What is the mass of ball B. Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20.
Meters per second in the same direction. M 03 kg. Meters per second collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10.
Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20 ms collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10ms in the same direction After the collision ball A moves at 10 ms and ball B at 15 ms in the same direction. For force F 5 N at angle A relative to u and time t 003 s the change of momentum. What is the magnitude of the net force required to bring the mass to a stop in 80 seconds.
What is the mass of ball. Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20 ms collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10ms in the same direction After the collision ball A moves at 10 ms and ball B at 15 ms in the same direction. What is the mass of ball B.
If the collision is elastic what is the velocity of a ball A and b ball B after the collision. What is the mass of ball B. 5 k g moving with speed of 2.
Click hereto get an answer to your question Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20 ms collides with ball B of unknown mass moving at 10ms in the same direction After the collision ball A moves at 10 ms and ball B at 15 ms in the same direction. Would doubling the mass or doubling the speed have a greater effect on the kinetic. A ball of mass 0640 kg moving east x direction with a speed of 300 ms collides head-on with a 0740 kg ball at rest.
After the collision ball A moves at 10. 0 m s strikes a rigid wall in a direction perpendicular to the wall and is reflected back after a perfectly elastic collision. Ball A of mass 50 kilograms moving at 20.
Meters per second and ball B at 15 meters per second both still in the same direction. Meters per second and ball B at 15 meters per second both still in the same direction. Physics questions and answers.
V 20 05cosA ms. Meters per second in the same direction. V_10 second ball moves with a velocity of v_2 in the initial direction of first ball then.
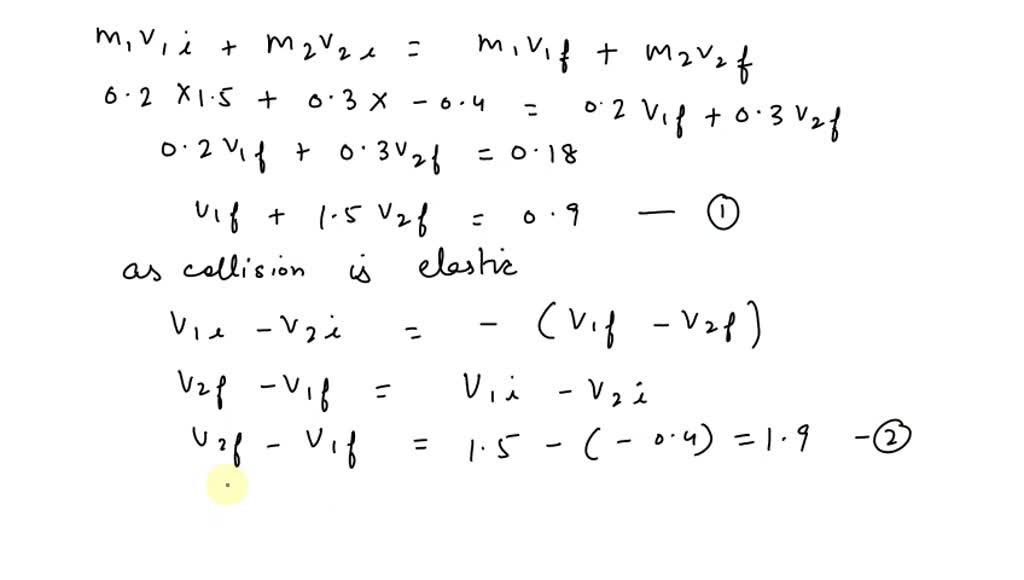
Solved A Ball Of Mass 0 200 Mathrm Kg With A Velocity Of 1 50 Hat Mathbf I Mathrm M Mathrm S Meets A Ball Of Mass 0 300 Mathrm Kg With A Velocity Of 0 400 Hat Mathbf I Mathrm M Mathrm S In

Ball A Of Mass 5 0 Kilograms Moving At 20 M S Collides With Ball B Of Unknown Mass Moving At 10m S In The Same Direction After The Collision Ball A Moves At 10

Solved 7 Ball A Of Mass 5 0 Kilograms Moving At 20 Meters Chegg Com

Ball A Of Mass 5 0 Kilograms Moving At 20 M S Collides With Ball B Of Unknown Mass Moving At 10m S In The Same Direction After The Collision Ball A Moves At 10
No comments for "Ball a of Mass 5.0 Kilograms Moving at 20"
Post a Comment